Key Vocabulary
Important vocabulary from the lessons
Unit 2… Binary/Data Terms
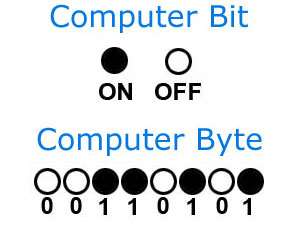
- Bits: the smallest unit of data that a computer can process and store, represented by a binary value 0 or 1
-
Bytes: a unit of data that is equivalent to eight bits
-
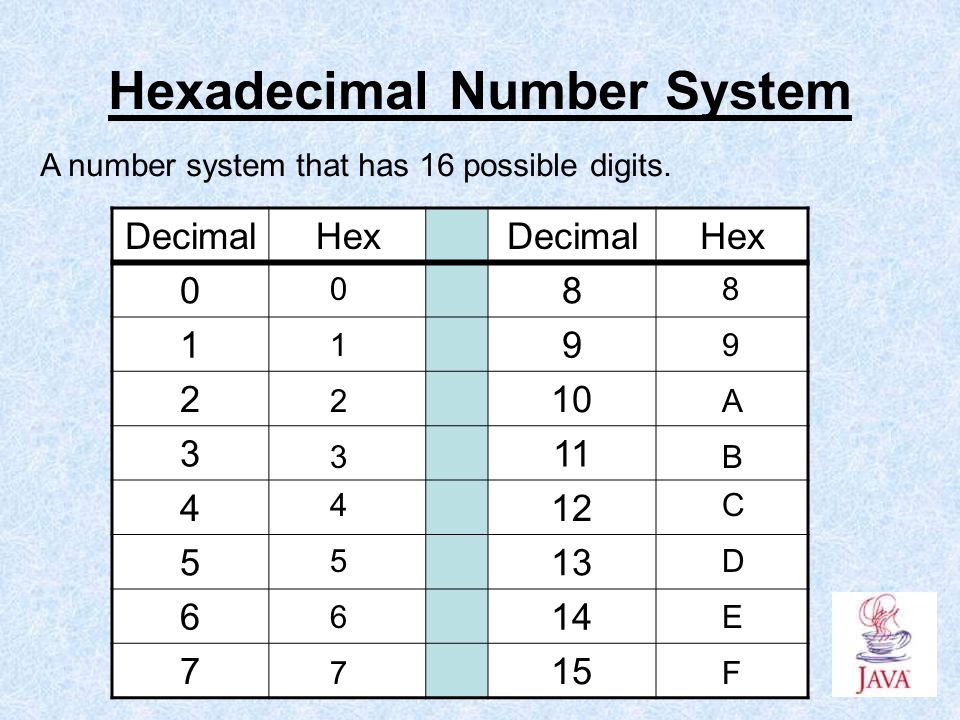
Hexadecimal: a number system with base 16 that uses 0-9 and letters A-F to represent data 10-15
-
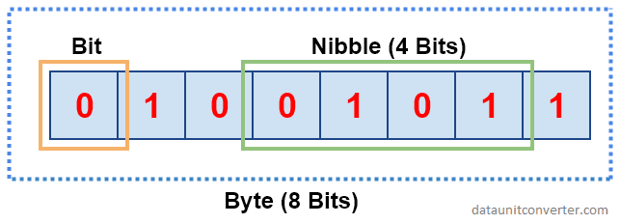
Nibbles: a combination of four binary digits or half of an 8-bit byte
-
Binary Numbers: base-two positional numeral system represented by a combination of 0’s and 1’s, it’s easier for computers to process and it takes up less space
- Unsigned Integer: whole numbers without a + or - sign, used when we know that the value that we are storing will always be non-negative
- Signed Integer: whole numbers that can be either positive or negative
- Floating Point: decimal numbers, can be positive or negative
-
Binary Data Abstractions: reducing parts of data to manage its complexity and reveal only a simplified representation
- Boolean: logical data type that can have only the values true or false
-
ASCII: AKA “American Standard Code for Information Interchange”, a code that uses numbers to represent characters, upper case and lower case hold different values, used for the representation of text (symbols, letters, digits…)
- ex. A = 65 and a = 97
-
Unicode: international character-encoding system to support the electronic interchange/processing/display of the written texts of different languages, written with a “U” followed by a plus sign and the number in hex
- ex. “Hello” = U+0048 U+0065 U+006C U+006C U+006F
-
RGB: red, blue, green, combination of the 3 colors can make any color, each range from 0 to 100 percent of full intensity
- ex. real life example is in LED light strips that people usually use to decorate their rooms. It has RGB lights that have different combinations and intensities to create different colors even like peach and teal

-
Data Compression: a reduction in the number of bits needed to represent data
-
Lossy: data in a file is removed and not restored to its original form after decompression, permanently removes redundant information
- JPEG images
-
Lossless: data in a file can be restored/rebuilt in its original form, data is rearranged to be more efficient
- PNG or GIF
-
Lossy: data in a file is removed and not restored to its original form after decompression, permanently removes redundant information
Unit 3… Algorithm/Programming Terms
- Variables: abstract storage location paired with an associated symbolic name, used to store information to be referenced and manipulated in a computer program
-
Data Types: a set of possible values and a set of allowed operations on it
- boolean, integer, string, floating point
- Assignment Operators: =, +=, -=, /=, *= and %=, used to assigning value to a variable
-
Managing Complexity with Variables: breaking down complex data and showing the essential parts at a simplified level
-
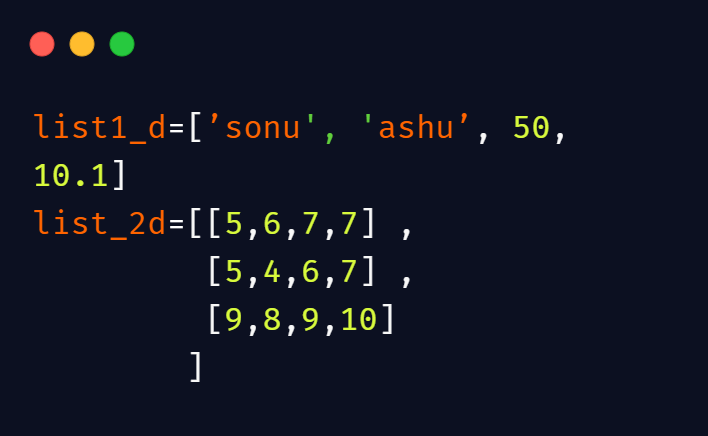
Lists: AKA an array, an abstract data type that represents a finite number of ordered values
- ex. in Python array = [“hello”, 17, true, apple]
-
2D Lists: AKA nested list or a list inside a list, each row can have different lengths and supports different data types
- Dictionaries: an abstract data type that defines an unordered collection of data as a set of key-value pairs, can hold booleans, strings, etc.
- Class: an object, with the name and defines a set of properties and methods that are common to all objects of one type
-
Lists: AKA an array, an abstract data type that represents a finite number of ordered values
- Algorithms: finite set of instructions that accomplish a specific task or perform tasks, idea of available alternatives and multiple ways to get to a solution
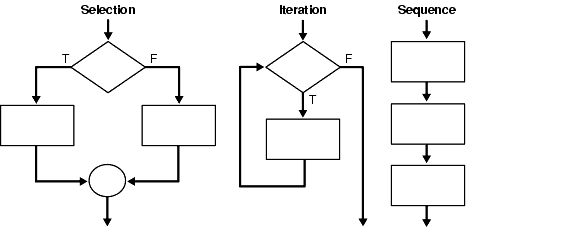
- Sequence: the whole code, start to finish
- Selection: a section of code is run only if a condition is met, when the programmer decides between two different outcomes
- Iteration: repeating a certain part of code until a condition is fulfilled
- Expressions: combinations of comparisons operators, functions, variables, or constants…like in math
- Comparison Operators: operators that compare values and return true or false, <, >, <=. >=, !=, ==
- Booleans Expressions: a logical statement that is either TRUE or FALSE, test data to see if it is equal to, greater than, or less than other data
- Boolean Selection: using the booleans to select subsets of data
-
Boolean Iteration: iterating based on a boolean expression
- expression always results in true or false
-
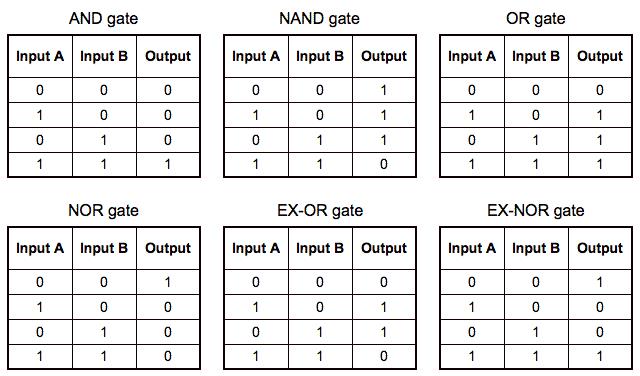
Truth Tables: a way of checking the logic of a circuit, it shows all possible combinations of inputs and outputs. You can produce truth tables for parts of a circuit to check the logic at any stage.
- Characters: a display unit of information that is equivalent to an alphabetic symbol or letter
- Strings: a type of variable made up of a sequence of characters
- Length: amount of characters in a string, amount of elements in a list
- Concatenation: combining two strings together
- Upper: changing a string to all upper case
- Lower: changing a string to all lower case
- Traversing Strings: the process of going through a String one character at a time, often using loops
-
Python: a coding language
- If: how you perform this sort of decision-making, allows for conditional execution of a statement or group of statements based on the value of an expression
- Elif: short for “else if” and is used when the first if statement isn’t true, but you want to check for another condition
- Else conditionals: used when you have to judge one statement on the basis of other, else keyword is used in conditional statements (if statements), and decides what to do if the condition is False
- Nested Selection Statements: an if statement placed inside another if statement
- For: for statement iterates over the members of a sequence in order, executing the block each time
- While loops with Range: run a piece of code while a condition is True, range method in python is used to create a sequence ranging between a certain limit
- While loops with List: repeating something over and over the items of a list, until a particular condition is satisfied
-
Combining loops with conditionals to Break, Continue: stops a code loop after it has looped x amount of times, and to later continue the code

- Procedural Abstraction: code sections/procedures, generalised by having variable parameters The idea is that we have code which can cope with a variety of different situations, depending on how its parameters are set when it is called.
- Python Def procedures: def defines a function
- Parameters: variables or placeholders for the actual values the function needs. When the function is called, these values are passed in as arguments.
- Return Values : a value that a function returns to the calling script or function when it completes its task