4.1 The Internet
Explaining how computers send and receive information through different systems, and how to facilitate the transfer of data.
Big Ideas/Topics
- How computing devices work together in a network.
- packet- a small amount of data sent over a network, includes source and destination info
- packet switching- the message/file is broken up into packets and sent in any order, then reassembled by the recipient’s device
- path- a sequence of directly connected computing devices that begins at the sender and ends at the receiver
- route- the process of finding a path
- bandwidth- the speed in which the packet and information will flow, like traffic in cars, in bits per second
- computer systems- a group of computing devices and programs working together for a joint purpose
- computer network- a type of computing system, a group of interconnected computing devices capable of sending/receiving data
- Computers connect to help make things easier
- Information is sent in packets because you cannot transmit data through the internet all at once, it has to be sent in chunks
- There are rules of transmitting data/a protocol
Protocol of transmitting data
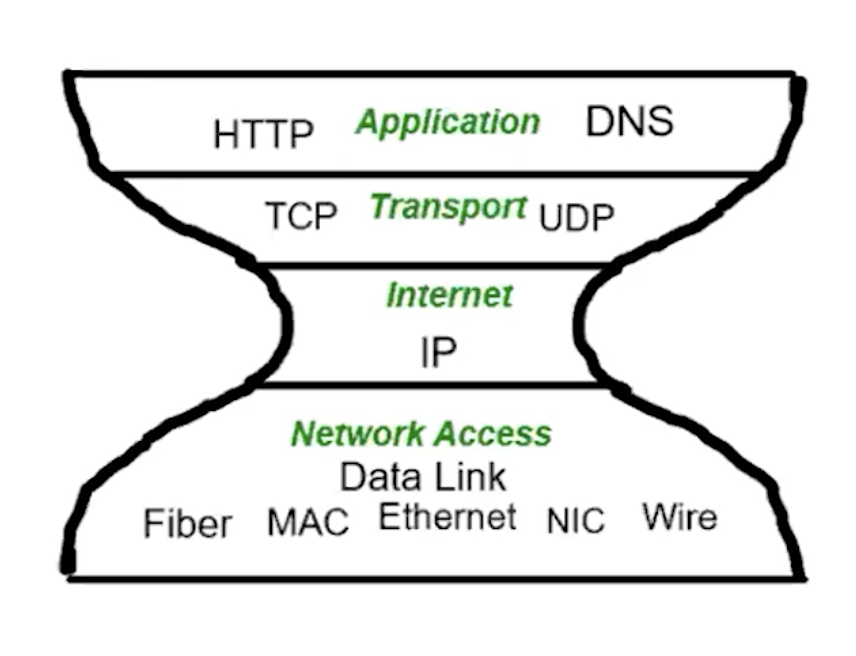
- Network Access: setting up things in the hardware, each having a unique MAC address, to pop from one card to another
- Internet Protocol: you have obtained your IP address, packets get set up with metadata, routers pass these messages to other routers to end up to the receiver/destination…there are many paths and internet is flexible/scalable
- Autonomous System (AS)- intranets want to talk to each other so they hop on these autonomous systems, controlled by internet providers –> want to join the internet
- Transport: how the packets are sent (sending an IP Address)
- TCP (stricter)- 3 way handshake, paying extra for it to be delivered
- UDP- best effort, just sending it in hopes of getting it delivered
- Application:
- DNS, domain name service- a database that maps the IP Numbers to names (.edu .com .gov .org)
- key protocols: http and https
Recap
Open standards and protocols enable different manufacturers (OSI models) and developers to build hardware and software that can communicate with hardware and software on the rest of the internet. IETF is a task force to set protocols, and keep it open to everyone. Routers help push things along, in a flexible way, determines on the way. A protocol is an agreed upon set of rules that specify the behavior of a system. UDP is faster, and does not guarantee transfers The World Wide Web is NOT the Internet. An HTTP is a protocol used by the World Wide Web.
Hard Questions