1.2 Program Function & Purpose
Explaining the different purposes of programs and how it works.
- Computing Innovations
- Purpose of Innovations
- Inputs to Programs
- Programs Receiving Input- events are triggered by some sort of action, which usually sends input to the program
- What dees Input accomplish?
- How does a program know what to do?
- What is a program?
- Difficult Problems
Computing Innovations
-
Applications
- Games
- Social Media
- Business
- Productivity
-
Physical Devices
- Computers
- Smart phones/tablets
- Smart “Things”
- Wearables (apple watches, things to help keep people alive/alert health or vitals)
-
Systems
- E-commerce (online shopping)
- Cloud services (files stored online)
- E-mail (communication)
Purpose of Innovations
Guidance
- Why does this computing innovation exist?
- safety, convenience, efficiency
- What problems does this computing innovation solve?
- does not have to be negative, an issue
- What does the computing innovation allow us to do that we could not do before?
Inputs to Programs
- touch/tactile
- swipe
- press
- audio
- voice recognition (siri)
- visual
- facial recognition
- text (including numbers)
- passwords
Programs Receiving Input- events are triggered by some sort of action, which usually sends input to the program
- mouse clicks
- swipes
- taps
- certain entries or keys together
- key words/phrases
- physical buttons
What dees Input accomplish?
- usually affects the output
- Must follow a sequence or series for it to work
How does a program know what to do?
- action triggers an event (Ring doorbell)
- the program jumps to the code according to the event –> directs you to different spots/segments (as they are called, not necessarily in order) –> output is triggered
What is a program?
- a collection of statements, often referred to as software
- needs to work for a variety of inputs and situations
- a statement is a single command
- a code segment is a group of statements
- can be in order or not, depending on coding language
Difficult Problems
- Consider the following code segment.
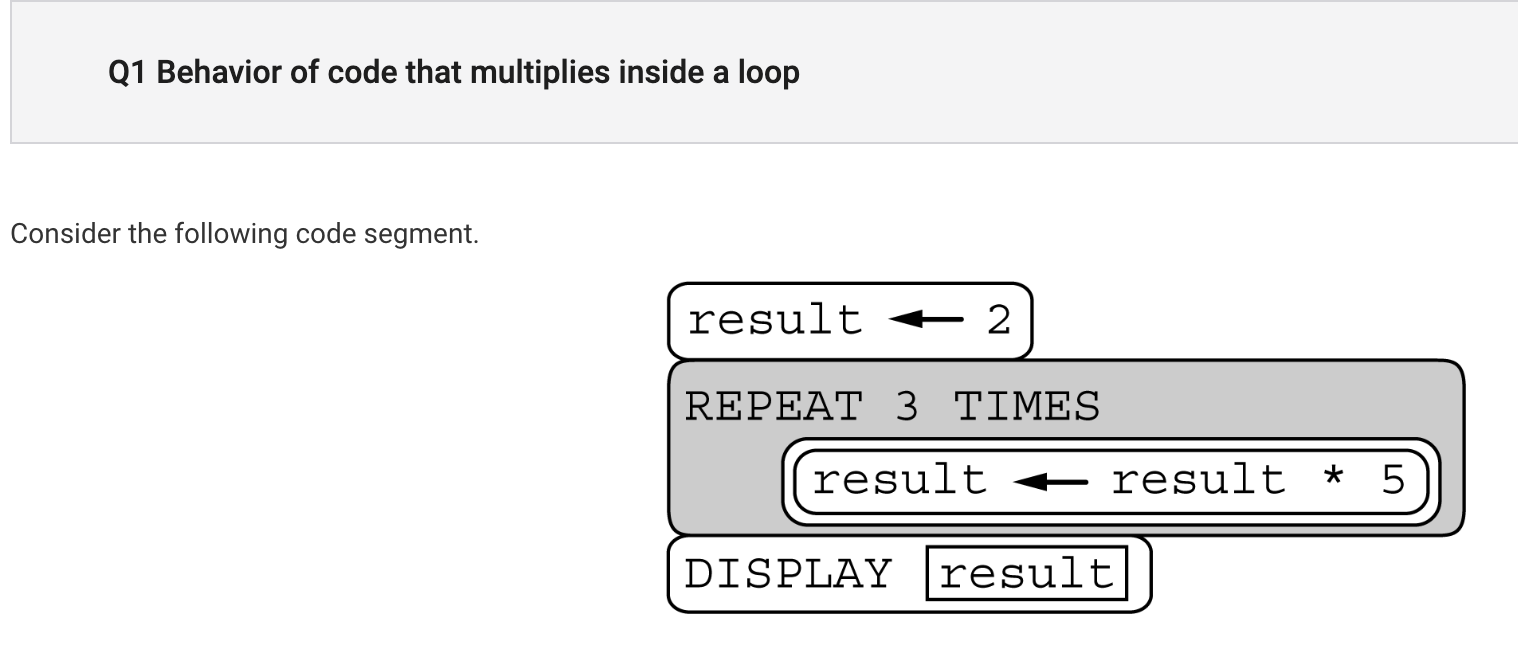
Which of the following best describes the behavior of the code segment?
A) The code segment displays the value of 2(5×3) by initializing result to 2 and then multiplying result by 3 a total of five times.
B) The code segment displays the value of 2(5×3) by initializing result to 2 and then multiplying result by 5 a total of three times.
C) The code segment displays the value of 2(5^3) by initializing result to 2 and then multiplying result by 3 a total of five times.
D) The code segment displays the value of 2(5^3) by initializing result to 2 and then multiplying result by 5 a total of three times.
- I chose B but the answer is D. I got confused with multiplication and exponents. You have the result of 5 but 3 times, and then that multiplied by 2
- A student wrote the following code segment, which displays true if the list myList contains any duplicate values and displays false otherwise.
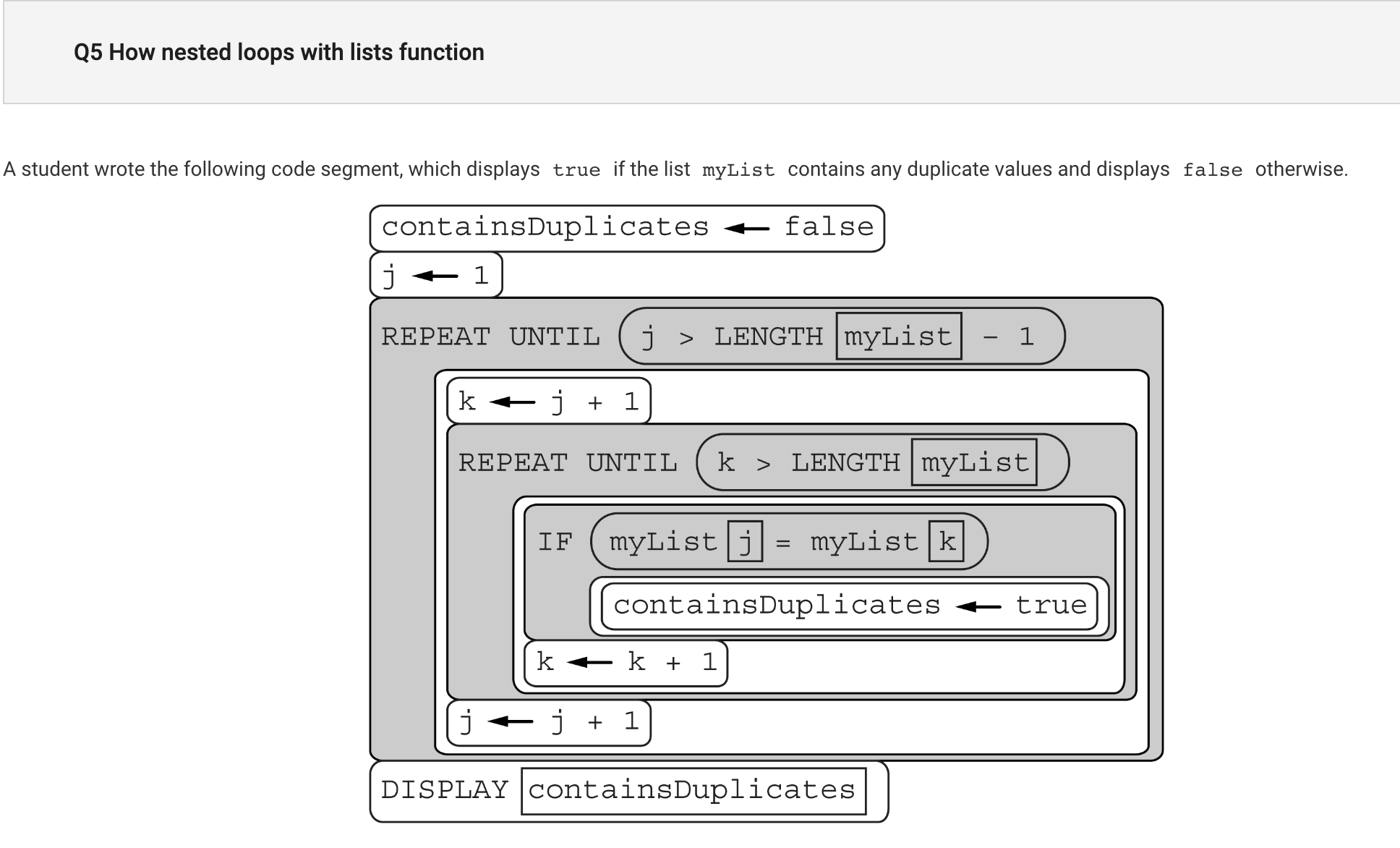 The code segment compares pairs of list elements, setting containsDuplicates to true if any two elements are found to be equal in value. Which of the following best describes the behavior of how pairs of elements are compared?
The code segment compares pairs of list elements, setting containsDuplicates to true if any two elements are found to be equal in value. Which of the following best describes the behavior of how pairs of elements are compared?
A) The code segment iterates through myList, comparing each element to all other elements in the list.
B) The code segment iterates through myList, comparing each element to all subsequent elements in the list.
C) The code segment iterates through myList, comparing each element to the element that immediately follows it in the list.
D) The code segment iterates through myList, comparing each element to the element that immediately precedes it in the list.
- I chose C but the answer is B. The code segment compares each element to every element after it, not just the one directly after.